NCM 103 Study Guide
General Introduction
- This study guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential concepts and principles in nursing as outlined in the NCM 103 curriculum, focusing on practical knowledge for the PNLE exam.
- It emphasizes the importance of clinical skills, patient care interventions, and relevant nursing procedures necessary for successful exam preparation.
Key Definitions
- Nursing: The protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities, prevention of illness and injury, alleviation of suffering through diagnosis and treatment of human responses.
- Clinical Skills: Specific procedures and techniques performed by nurses to provide care and treatment to patients.
- Patient Care Interventions: Actions taken by nurses to enhance patient outcomes, including assessments, treatments, and education.
Key Principles
- Holistic Care: Addressing the physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs of patients.
- Evidence-Based Practice: Utilizing the best current evidence in making decisions about patient care.
- Patient-Centered Care: Involving patients in their own care planning and decision-making processes.
Relevance to the PNLE Exam
- Understanding clinical skills and patient care interventions is crucial as they are frequently tested in the PNLE, particularly in scenarios involving patient assessment and management.
Common Misconceptions
- Misconception: Nursing is solely about following physician orders.
- Clarification: Nurses are critical thinkers who assess, plan, implement, and evaluate patient care independently and collaboratively.
Quick Tips
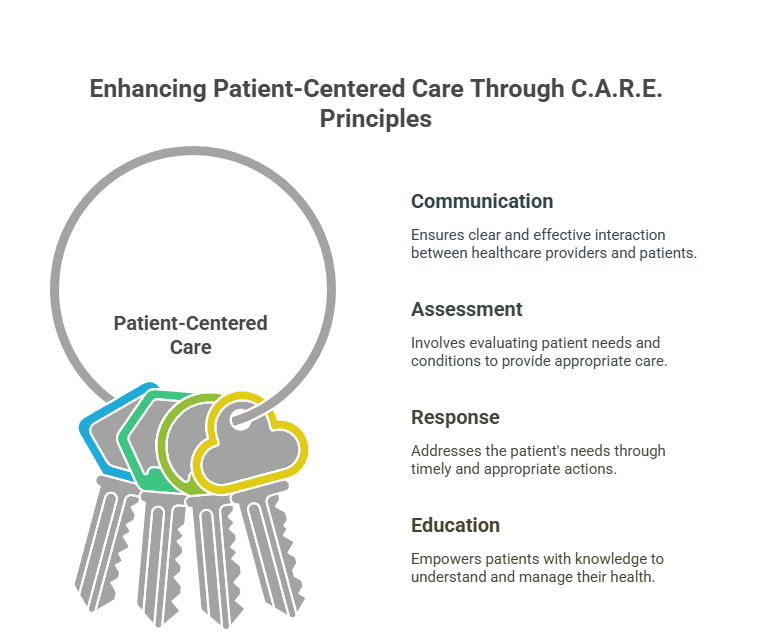
- Remember the acronym C.A.R.E. for patient-centered care: Communication, Assessment, Response, Education.
Practice Questions
- Which of the following best describes evidence-based practice in nursing?
- A) Following traditional methods of care
- B) Using the best available evidence to make clinical decisions
- C) Relying solely on physician orders
- D) Implementing care based on personal experience
Correct Answer: B – Evidence-based practice involves integrating clinical expertise with the best available evidence and patient values.
- What is the primary focus of holistic care?
- A) Treating the physical symptoms of a disease
- B) Addressing all aspects of a patient’s well-being
- C) Following strict medical guidelines
- D) Prioritizing medication administration
Correct Answer: B – Holistic care considers the whole person, including emotional, social, and spiritual needs.
Take-Home Message
- A comprehensive understanding of nursing principles and clinical skills is essential for effective patient care and success in the PNLE exam.
1. Nursing Procedures
Introduction
Nursing procedures are fundamental skills that every nurse must master to provide safe and effective patient care. This section will cover essential nursing procedures relevant to the PNLE, ensuring that nursing graduates are well-prepared for the exam.
Key Definitions
- Vital Signs:strong> Measurements of the body’s most basic functions, including temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure.
- Medication Administration: The process of giving medications to patients, adhering to the “”five rights”” (right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right time).
- Basic Nursing Skills: Essential skills required for patient care, including wound care, catheterization, and patient positioning.
Key Principles
- Accuracy: Ensuring precise measurements and administration to prevent errors.
- Safety: Prioritizing patient safety during all procedures.
- Patient-Centered Care: Involving patients in their care and ensuring their comfort.
Relevance to the PNLE Exam
- Mastery of nursing procedures is frequently tested in the PNLE, particularly in areas related to vital signs and medication administration. Understanding these concepts is crucial for success on the exam.
Topic Overview
Understanding proper nursing procedures is crucial for accurate assessments and interventions.
In-Depth Review
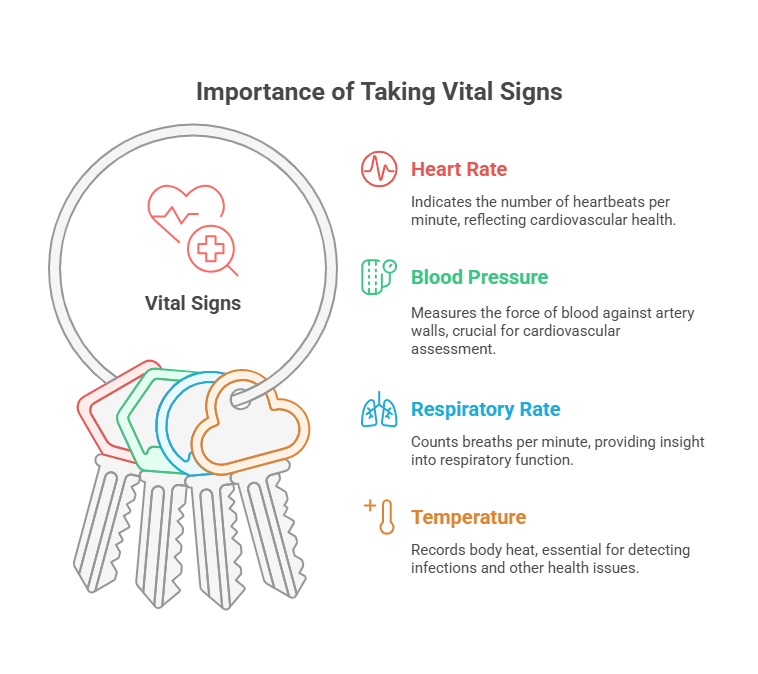
- Know the normal ranges:
- Temperature: 36.1°C to 37.2°C (97°F to 99°F)
- Pulse: 60 to 100 beats per minute
- Respiration: 12 to 20 breaths per minute
- Blood Pressure: 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg
- Techniques for measuring each vital sign.
- Administering Medications:
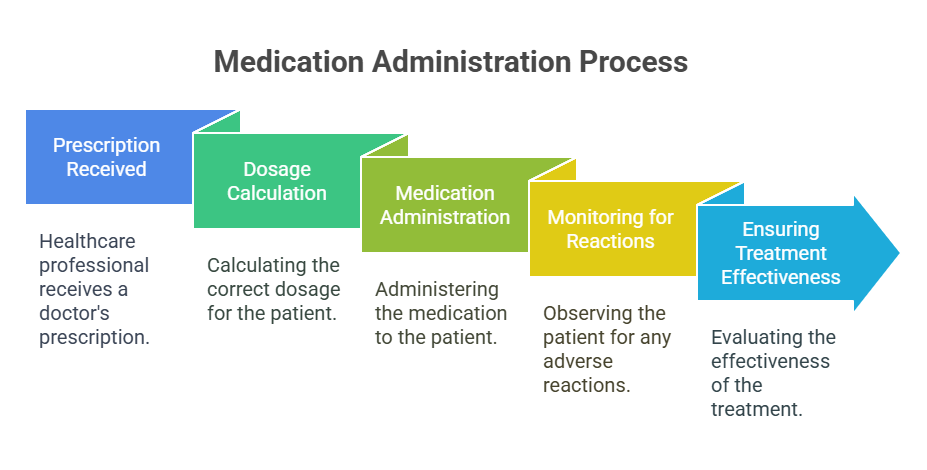
- Review the rights of medication administration:
- Right patient
- Right drug
- Right dose
- Right route
- Right time
- Common routes: oral, IV, IM.
- Performing Basic Nursing Skills:
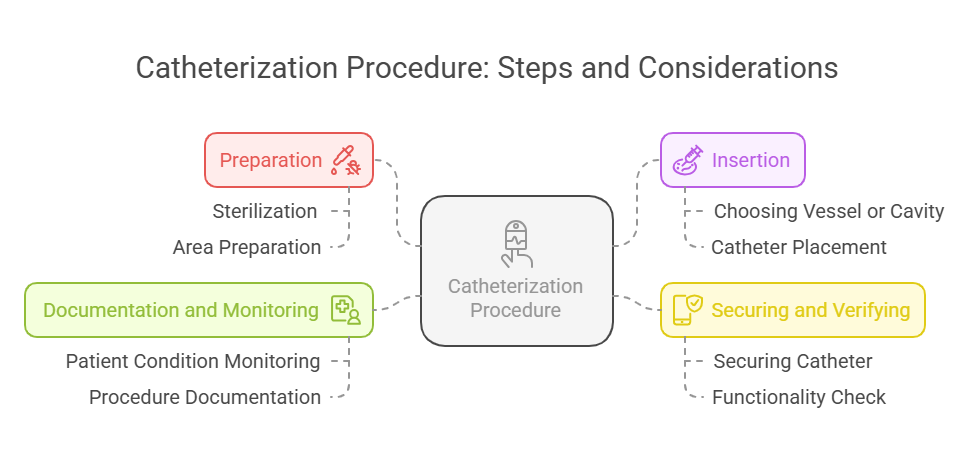
- Catheterization procedures
- Proper patient positioning
Common Misconceptions
- Misunderstanding Vital Sign Order: Some may believe that the order of taking vital signs is flexible; however, a consistent sequence helps ensure accuracy and reliability.
Practice Questions
- What is the correct sequence for taking vital signs?
- A) Temperature, Pulse, Respiration, Blood Pressure
- B) Blood Pressure, Temperature, Pulse, Respiration
- C) Pulse, Blood Pressure, Temperature, Respiration
- D) Respiration, Pulse, Blood Pressure, Temperature
Correct Answer: A) Temperature, Pulse, Respiration, Blood Pressure.
Rationale: This order is standard practice for comprehensive assessment.
- What is the normal range for adult blood pressure?
- A) 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg
- B) 120/80 mmHg to 140/90 mmHg
- C) 130/80 mmHg to 150/95 mmHg
- D) 110/70 mmHg to 130/85 mmHg
Correct Answer: A) 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg.
Rationale: Understanding normal blood pressure ranges aids in identifying hypertension or hypotension.
Quick Tips
- Always double-check vital signs before reporting.
- Use the “”five rights”” as a checklist for medication administration.
Memory Aid
- Mnemonic: “”Vital Signs: TPR-BP”” (Temperature, Pulse, Respiration, Blood Pressure).
Take-Home Message
Proficiency in nursing procedures is vital for effective patient assessment and care.
2. Nursing Process
Introduction
The nursing process is a systematic approach to patient care that guides nurses in providing effective interventions. It is essential for delivering individualized care and is a foundational concept for nursing practice and education. This section focuses on applying the nursing process in various settings, emphasizing its relevance to the PNLE.
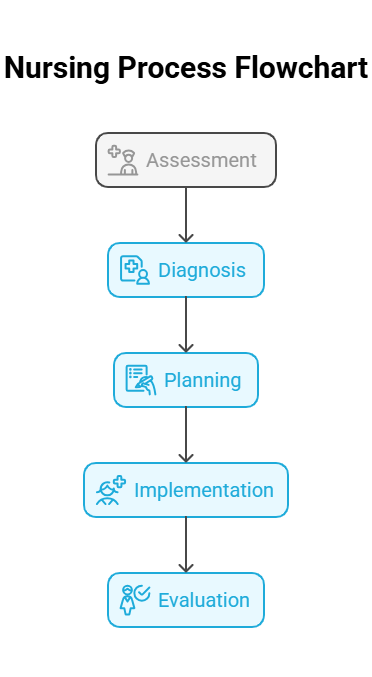
Key Definitions
- Nursing Process: A systematic method used by nurses to plan and provide patient care.
- Assessment: The first step of the nursing process, involving the collection of patient data.
- Diagnosis: The identification of patient problems based on assessment data.
- Planning: The development of a care plan with measurable goals.
- Implementation: The execution of the care plan.
- Evaluation: The assessment of the effectiveness of the care plan.
Key Principles
- The nursing process is patient-centered, focusing on the unique needs of each individual.
- It is dynamic, allowing for adjustments based on patient responses and outcomes.
- Each step is interconnected, with the outcome of one step influencing the next.
Relevance to the PNLE Exam
- The nursing process is frequently tested in PNLE, particularly the steps involved and their definitions.
- Understanding the nursing process is crucial for answering questions related to patient care scenarios.
Relation to Other Topics
- The nursing process is often confused with clinical reasoning. While both involve decision-making, the nursing process is a structured framework, whereas clinical reasoning is a broader cognitive process.
- Care Plans are a direct output of the nursing process, specifically from the planning phase.
Practice Questions
- PNLE Question: Which step of the nursing process involves setting measurable goals for patient care?
- A) Assessment
- B) Diagnosis
- C) Planning
- D) Implementation
Correct Answer: C) Planning
Rationale: The planning phase is where specific, measurable goals are established for patient care.
- What is the primary purpose of the assessment phase in the nursing process?
- A) To implement interventions
- B) To evaluate outcomes
- C) To collect patient data
- D) To establish nursing diagnoses
Correct Answer: C) To collect patient data
Rationale: The assessment phase is crucial for gathering data that informs all subsequent steps in the nursing process.
Memory Aid
- Mnemonic: “”ADPIE”” (Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, Evaluation) – a simple way to remember the steps of the nursing process.
Common Misconceptions
- A frequent misunderstanding is that the nursing process is linear; however, it is cyclical and may require revisiting earlier steps based on evaluation outcomes.
Quick Tips
- Always document findings during the assessment phase to ensure accurate data collection.
- In the planning phase, ensure goals are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
Take-Home Message
Mastery of the nursing process is essential for effective patient care and successful PNLE performance.
3. Nursing Interventions
Introduction
Nursing interventions are essential actions taken by nurses to enhance patient health outcomes. This section explores various interventions aimed at promoting both physiological and psychosocial health, ensuring a holistic approach to patient care.
Key Definitions
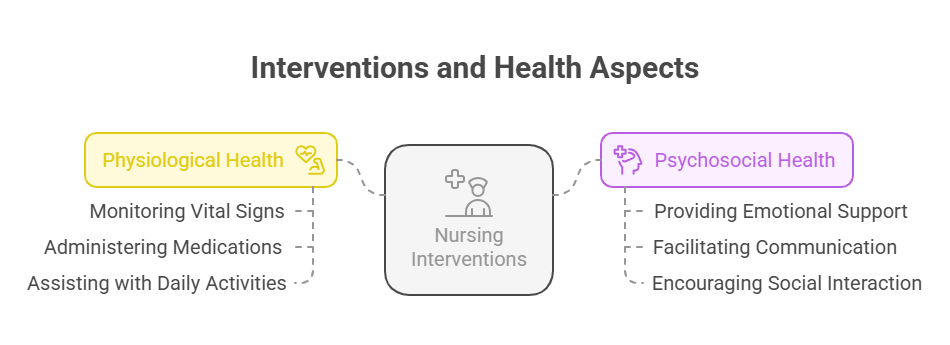
- Nursing Interventions: Actions taken by nurses to improve patient health outcomes.
- Physiological Health: The physical well-being of a patient, including bodily functions and processes.
- Psychosocial Health: The emotional and social well-being of a patient, encompassing mental health and social interactions.
Key Principles
- Holistic Care: Addressing both physical and emotional needs of patients.
- Patient-Centered Approach: Tailoring interventions to meet individual patient needs and preferences.
- Evidence-Based Practice: Utilizing research and clinical guidelines to inform nursing interventions.
Relevance to the PNLE Exam
- Focus on high-yield interventions commonly tested in the PNLE, such as pain management, anxiety reduction, and patient education.
Topic Overview
Effective nursing interventions can significantly impact patient recovery and well-being. Understanding the types of interventions and their applications is crucial for nursing practice and exam success.
In-Depth Review
- Promote Healthy Physiologic Responses:
- Implement interventions such as:
- Pain management techniques (e.g., medication, non-pharmacological methods).
- Mobility assistance to prevent complications like pressure ulcers.
- Promote Healthy Psychosocial Responses:
- Utilize:
- Therapeutic Communication: Engaging in active listening and providing emotional support.
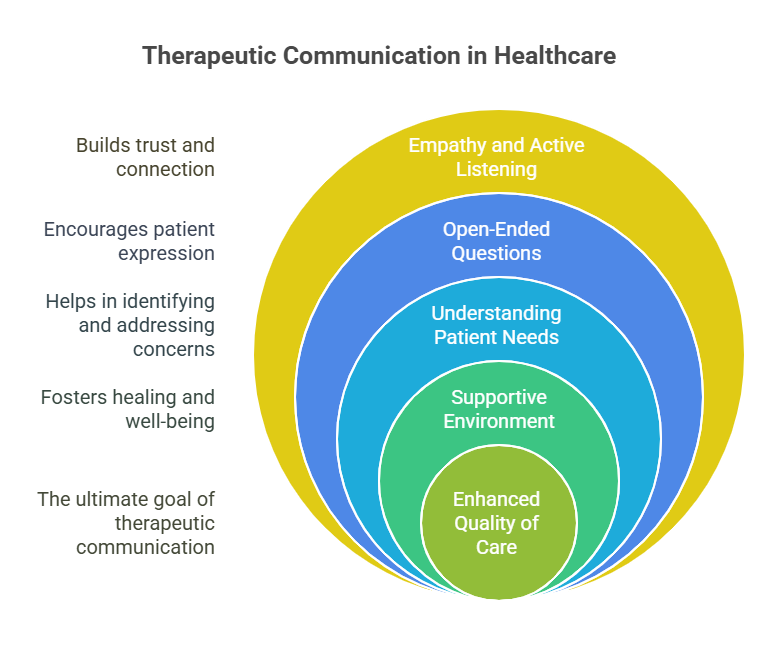
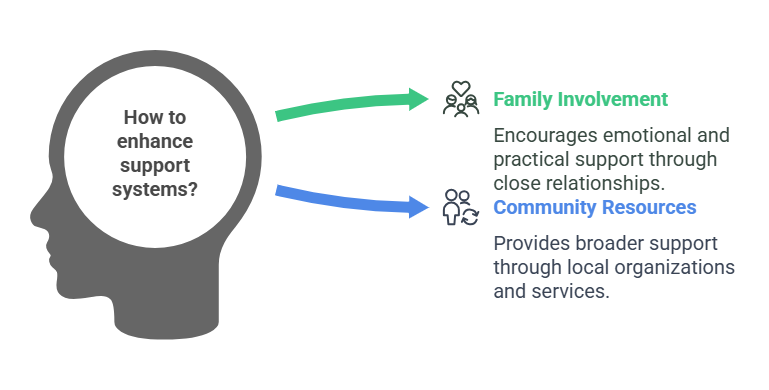
- Support Systems: Encouraging family involvement and community resources.
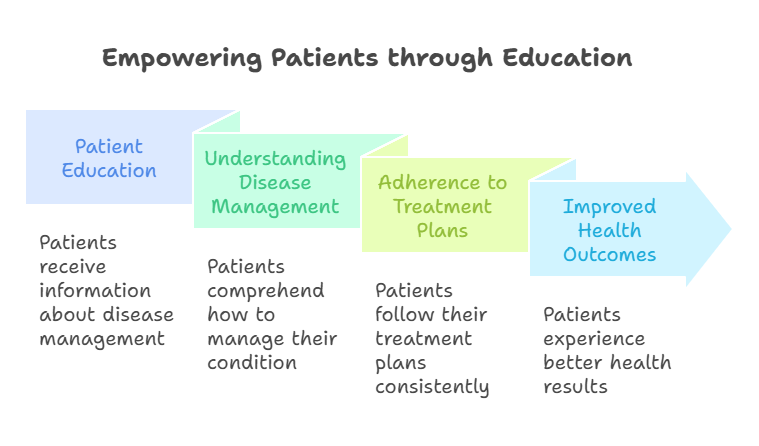
- Patient Education:
- Teach patients about:
- Their conditions and treatment options.
- Self-care strategies to manage their health effectively.
Practical Application
- Relevance to Filipino Healthcare:
- Culturally sensitive interventions can improve trust and cooperation between nurses and patients, fostering a supportive environment.
- Providing Education:
- Empowering patients through education on disease management can enhance adherence to treatment plans and improve health outcomes.
Practice Questions
- What is an effective nursing intervention for a patient with chronic pain?
- A) Administering pain medications as prescribed
- B) Advising the patient to rest completely
- C) Encouraging the patient to ignore the pain
- D) Avoiding discussions about pain management
Correct Answer: A) Administering pain medications as prescribed
Rationale: Administering prescribed pain medications is a direct intervention to manage chronic pain effectively.
- Which intervention is most appropriate for a patient experiencing anxiety?
- A) Administering antianxiety medication
- B) Encouraging deep breathing exercises
- C) Isolating the patient from others
- D) Ignoring the patient’s concerns
Correct Answer: B) Encouraging deep breathing exercises
Rationale: Deep breathing exercises can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
Memory Aid
- Mnemonic: “”Caring = Assess + Act””
- This highlights the importance of assessing patient needs before taking appropriate action.
Common Misconceptions
- Misconception: All nursing interventions require a physician’s order.
- Clarification: Many interventions, especially those related to education and emotional support, can be initiated by nurses independently.
Quick Tips
- Always assess the patient’s needs before implementing any intervention.
- Engage in therapeutic communication to understand patient concerns better.
Take-Home Message
Effective nursing interventions are critical for promoting optimal health outcomes, emphasizing the importance of a holistic and patient-centered approach.
3. Leadership and Management
This section focuses on the critical aspects of leadership and management in nursing, essential for effective practice and successful PNLE preparation.
3.1. Role of the Nurse as Leader/Manager
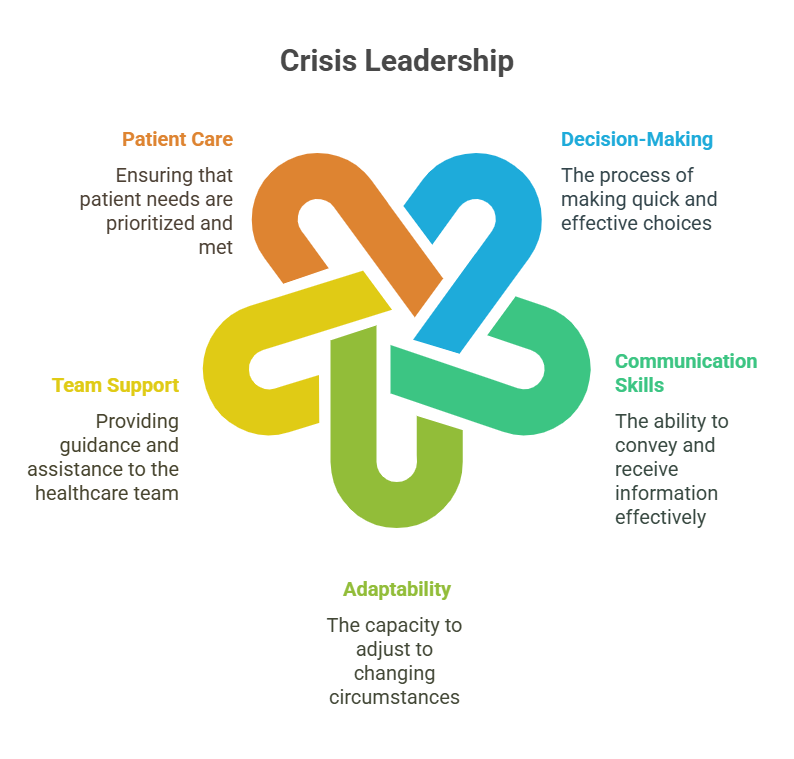
- 3.1.1. Crisis Leadership
- Key Definition: The ability to guide and support a team during emergencies or unexpected situations.
- Key Principles:
- Quick decision-making
- Clear communication
- Team cohesion
- 3.1.2. Data-Driven Decision Making
- Key Definition: Utilizing data and evidence to inform nursing practices and decisions.
- Key Principles:
- Collecting relevant data
- Analyzing trends
- Implementing evidence-based practices
- 3.1.3. Delegation and Supervision
- Key Definition: Assigning tasks to team members while maintaining accountability for patient care.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding team members’ competencies
- Clear communication of expectations
- Monitoring outcomes
- 3.1.4. Emotional Intelligence
- Key Definition: The ability to recognize and manage one’s own emotions and the emotions of others.
- Key Principles:
- Self-awareness
- Empathy
- Relationship management
- 3.1.5. Ethical Leadership
- Key Definition: Leading with integrity and making decisions based on ethical principles.
- Key Principles:
- Upholding ethical standards
- Promoting fairness
- Encouraging transparency
- 3.1.6. Leadership Skills
- Key Definition: Essential skills that enable effective leadership in nursing.
- Key Principles:
- Communication
- Conflict resolution
- Visionary thinking
- 3.1.7. Leading Change
- Key Definition: The ability to guide teams through transitions and improvements in practice.
- Key Principles:
- Assessing the need for change
- Engaging stakeholders
- Evaluating outcomes
- 3.1.8. Resource Allocation
- Key Definition: The strategic distribution of resources to optimize patient care.
- Key Principles:
- Identifying resource needs
- Prioritizing based on patient acuity
- Ensuring efficient use of resources
3.2. Positive Practice Environment
- 3.2.1. Characteristics of a Healthy Workplace
- Key Definition: Attributes that contribute to a supportive and productive work environment.
- Key Principles:
- Open communication
- Team collaboration
- Recognition and support
- 3.2.2. Managing Burnout
- Key Definition: Strategies to prevent and address burnout among nursing staff.
- Key Principles:
- Promoting work-life balance
- Providing mental health resources
- Encouraging self-care practices
Relevance to the PNLE Exam
- Understanding leadership and management principles is crucial for questions related to team dynamics, ethical decision-making, and patient safety. Focus on scenarios that involve crisis management and delegation.
Practice Questions
- Which of the following is a key characteristic of effective crisis leadership?
- A) Avoiding conflict
- B) Quick decision-making
- C) Ignoring team input
- D) Maintaining status quo
Correct Answer: B) Quick decision-making
Rationale: Effective crisis leadership requires rapid and informed decision-making to ensure patient safety and team coordination.
- What is the primary benefit of data-driven decision-making in nursing?
- A) It reduces the need for teamwork.
- B) It enhances patient outcomes through evidence-based practices.
- C) It eliminates the need for patient assessments.
- D) It focuses solely on financial aspects.
Correct Answer: B) It enhances patient outcomes through evidence-based practices.
Rationale: Data-driven decision-making allows nurses to implement interventions that are proven to be effective, ultimately improving patient care.
Common Misconceptions
- Misconception: Leadership is only for those in formal management positions.
- Clarification: All nurses can exhibit leadership qualities, regardless of their title, by influencing and guiding their peers.
Quick Tips
- Clarification Effective leaders are not just managers; they inspire and empower their teams.
- Mnemonic: LEAD – Listen, Empower, Assess, Decide.
Take-Home Message
Effective leadership and management in nursing are essential for fostering a positive practice environment and ensuring high-quality patient care.
NLExprt.com


















