NCM 101 Study Guide
General Introduction
- This study guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the
essential nursing concepts and
theories necessary for the Philippine Nursing Licensure
Examination (PNLE). - It emphasizes holistic nursing assessment, including
physical, mental,
psychosocial, and nutritional evaluations,
aligning with the Filipino healthcare context. - The guide serves as a structured resource to enhance understanding and
retention of critical nursing knowledge, preparing students for both the
PNLE and practical nursing roles.
Key Definitions
- Holistic Nursing Assessment: An approach that considers the
whole person, including their physical, emotional, social, and spiritual
needs. - Nursing Theories: Frameworks that guide nursing practice,
education, and research, providing a foundation for understanding patient
care. - PNLE: Philippine Nursing Licensure Examination, a
standardized test for aspiring nurses in the Philippines to assess their
competence and readiness for practice.
Key Principles
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Assessing all dimensions of a
patient’s health to provide thorough care. - Patient-Centered Care: Focusing on the individual needs and
preferences of patients in the nursing process. - Integration of Knowledge: Utilizing nursing theories and
clinical practice to inform decision-making and improve patient outcomes.
Take-Home Message
Holistic nursing assessment is essential for delivering comprehensive care and
preparing for the PNLE, ensuring nurses meet the diverse needs of patients.
Relevance to the PNLE Exam
- Expect questions on the components of holistic assessments and their
application in various clinical scenarios. - Familiarity with nursing theories may be tested in relation to patient care
strategies.
Common Misconceptions
- Misconception: Holistic assessment only involves physical
examination.- Clarification: It includes mental, psychosocial, and
nutritional evaluations as well.
Quick Tips
- Remember the acronym PMPN (Physical, Mental, Psychosocial,
Nutritional) to recall the components of holistic assessment.
Practice Questions
- Which of the following is NOT a component of holistic nursing assessment?
- A) Physical evaluation
- B) Spiritual assessment
- C) Financial status
- D) Nutritional evaluation
Correct Answer: C) Financial status Rationale:
Holistic assessment focuses on health-related aspects rather than financial
considerations.
- What is the primary purpose of nursing theories in practice?
- A) To provide a strict guideline for nurses
- B) To enhance understanding and improve patient care
- C) To limit the scope of nursing practice-
- D) To replace clinical judgment
Correct Answer: B) To enhance understanding
and improve patient care Rationale: Nursing theories serve as
frameworks that guide practice and inform clinical decision-making.
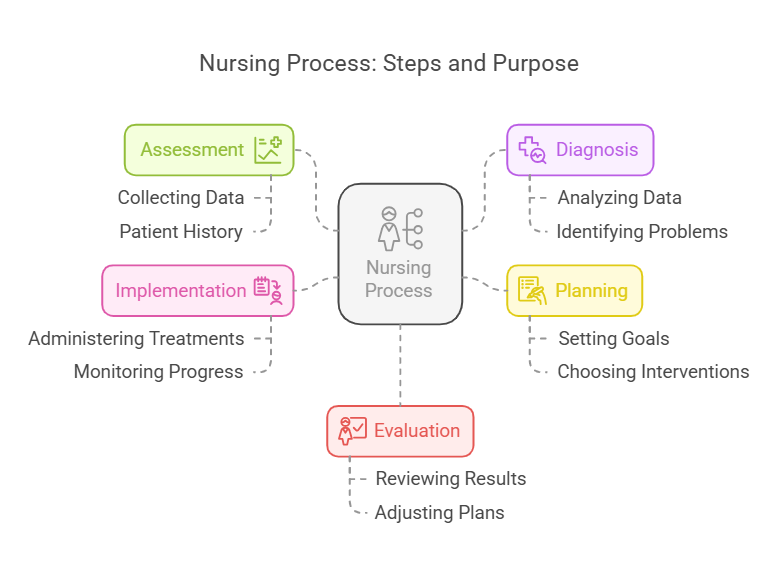
1. Introduction to Health Assessment
1.1 Overview of Nursing Process (ADPIE)
- Introduction: The nursing process is a
systematic approach that guides nurses in delivering patient care.
Understanding this framework is crucial for effective health assessments and
interventions.
- Key Definitions:
- Assessment: The systematic collection of patient data.
- Diagnosis: Identifying patient problems based on
assessment data. - Planning: Developing a strategy for patient care.
- Implementation: Executing the care plan.
- Evaluation: Assessing the effectiveness of the care
provided.
- Key Principles:
- The nursing process consists of five key steps:
Assessment, Diagnosis,
Planning, Implementation, and
Evaluation (ADPIE). - Each step is interconnected and essential for delivering comprehensive
patient care.
- Take-Home Message: Mastering the nursing process is
essential for conducting thorough health assessments and developing
appropriate care plans. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Understanding the nursing
process is frequently tested, particularly the correct sequence of steps. - Practice Question: What is the correct sequence of the
nursing process?- A) Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, Evaluation
- B) Diagnosis, Assessment, Planning, Implementation, Evaluation
- C) Planning, Implementation, Evaluation, Diagnosis, Assessment
- D) Implementation, Evaluation, Diagnosis, Assessment, Planning
Correct Answer: A) Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning,
Implementation, Evaluation. Rationale: This is the standard
sequence of the nursing process.
1.2 Types of Health Assessments
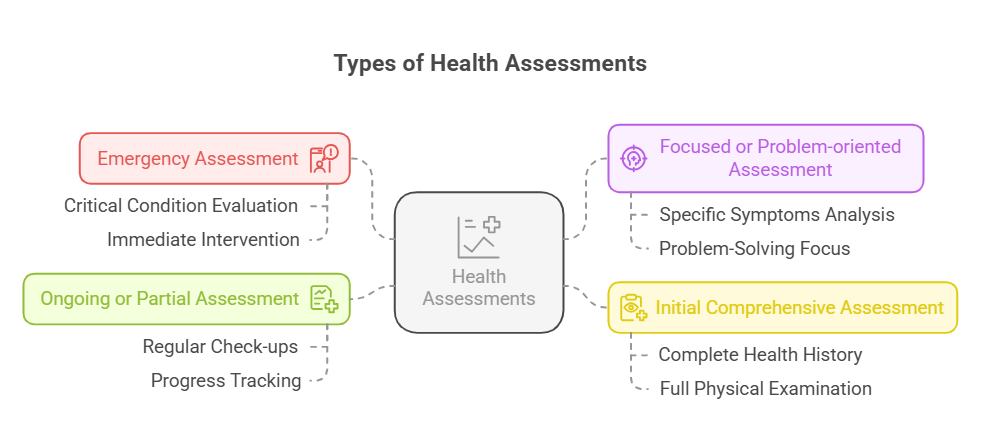
1.2.1 Emergency Assessment
- Introduction: Emergency assessments are
critical in acute situations where rapid evaluation is necessary. These
assessments help prioritize immediate care needs. - Key Definitions:
- Emergency Assessment: A quick evaluation to identify
life-threatening conditions.
- Key Principles:
- Focus on identifying life-threatening conditions quickly.
- Prioritize interventions based on assessment findings.
- Take-Home Message: Emergency assessments are vital for
guiding immediate interventions in critical situations. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions often focus on
prioritization in emergency scenarios. - Practice Question: In an emergency situation, which
assessment should be prioritized?- A) Full body assessment
- B) Focused assessment on the presenting problem
- C) Comprehensive health history
- D) Routine vital signs check
Correct Answer: B) Focused assessment on the presenting
problem. Rationale: This approach allows for rapid
identification of critical issues.
1.2.2 Focused or Problem-oriented Assessment
- Introduction: Focused assessments target
specific issues or symptoms. This approach is essential for efficient and
effective patient care. - Key Definitions:
- Focused Assessment: An assessment that concentrates on a
specific problem.
- Key Principles:
- Gather relevant information about a specific issue.
- Facilitate targeted interventions based on findings.
- Take-Home Message: Focused assessments streamline care by
addressing specific patient concerns. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on appropriate
assessment types based on patient presentations. - Practice Question: A patient presents with chest pain. What
type of assessment is most appropriate?- A) Comprehensive assessment
- B) Focused assessment
- C) Emergency assessment
- D) Routine assessment
Correct Answer: B) Focused assessment.
Rationale: This assessment is designed to address specific
symptoms.
1.2.3 Initial Comprehensive Assessment
- Introduction: The
initial comprehensive assessment provides a complete
picture of the patient’s health status and serves as the foundation for all
subsequent care. - Key Definitions:
- Comprehensive Assessment: A thorough evaluation including
health history and physical examination.
- Key Principles:
- Establish a baseline for future assessments.
- Identify all health issues and concerns.
- Take-Home Message: The initial comprehensive assessment is
crucial for individualized care planning. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Understanding the components
and goals of comprehensive assessments is often tested. - Practice Question: What is the primary goal of an initial
comprehensive assessment?- A) To diagnose a condition
- B) To establish a baseline for future assessments
- C) To implement care plans
- D) To evaluate treatment effectiveness
Correct Answer: B) To establish a baseline for future
assessments.
Rationale: This provides a reference point
for ongoing evaluations.
1.2.4 Ongoing or Partial Assessment
- Introduction: Ongoing assessments are
essential for monitoring changes in a patient’s condition over time,
ensuring that care remains relevant and effective. - Key Definitions:
- Ongoing Assessment: Continuous evaluation of a patient’s
health status.
- Key Principles:
- Regularly evaluate the patient’s condition.
- Adjust care plans based on assessment findings.
- Take-Home Message: Ongoing assessments are vital for
adapting care to changing patient needs. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions may focus on the
timing and purpose of ongoing assessments. - Practice Question: When should ongoing assessments be
performed?- A) Only at admission
- B) At regular intervals or when there are changes in the patient’s
condition - C) Only when the patient requests it
- D) At discharge
Correct Answer: B) At regular intervals or when there are
changes in the patient’s condition.
Rationale: This
ensures timely updates to the care plan.
1.3 Nurses’ Role in Health Assessment
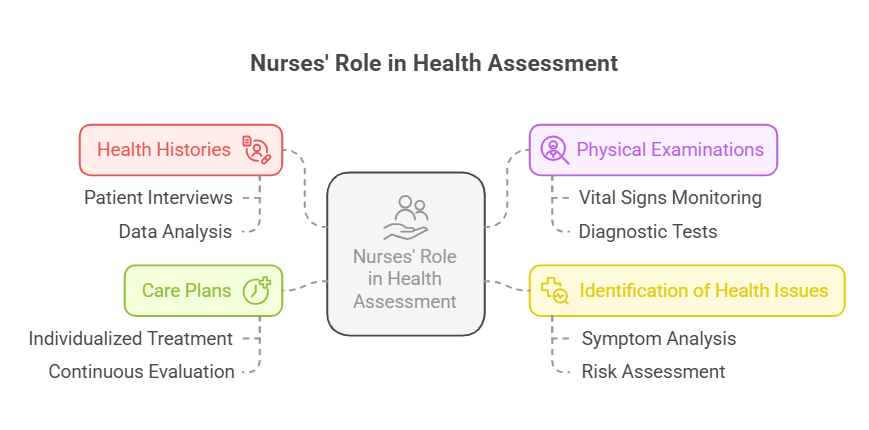
1.3.1 Obtain Patient History
- Introduction: Gathering a thorough
patient history is vital for understanding the patient’s
health context and guiding clinical decision-making.
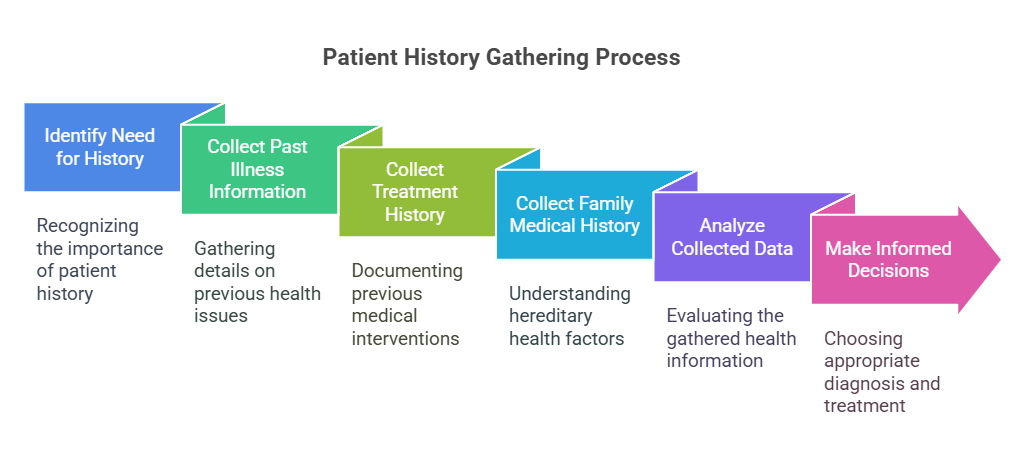
- Key Definitions:
- Patient History: A comprehensive account of the patient’s
medical, family, and social background.
- Key Principles:
- Collect detailed information to inform care.
- Use history to identify potential health risks.
- Take-Home Message: A comprehensive patient history is
foundational for effective nursing care. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on the
components of a complete patient history. - Practice Question: Which of the following is NOT typically
included in a patient history?- A) Medical history
- B) Family history
- C) Social history
- D) Personal preferences for food
Correct Answer: D) Personal preferences for
food.
Rationale: While relevant, it is not a standard
component of medical history.
1.3.2 Perform Physical Exam
- Introduction: Conducting a
physical examination is a fundamental skill for nurses,
allowing for the identification of health issues that may not be reported by
the patient.
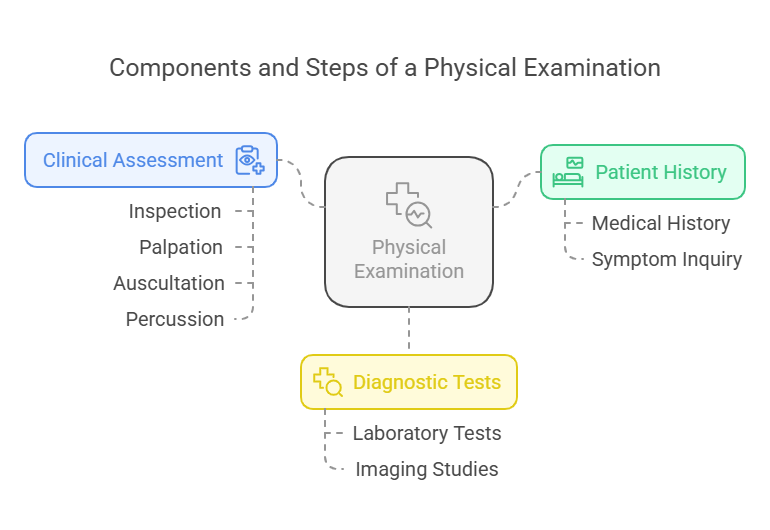
- Key Definitions:
- Physical Examination: A systematic assessment of the body
to identify health problems.
- Key Principles:
- Use a variety of techniques to assess different body systems.
- Document findings accurately to inform care.
- Take-Home Message: Physical exams are essential for
detecting health issues early. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions often focus on the
techniques and purposes of physical examinations. - Practice Question: What is the primary purpose of a
physical examination?- A) To establish a rapport with the patient
- B) To identify potential health problems
- C) To document patient history
- D) To provide patient education
Correct Answer: B) To identify potential health problems.
Rationale: The primary goal is to uncover health issues
through assessment.
1.3.3 Develop Care Plan
- Introduction: Developing a care plan is
essential for delivering personalized patient care, outlining the goals and
interventions tailored to the patient’s needs.
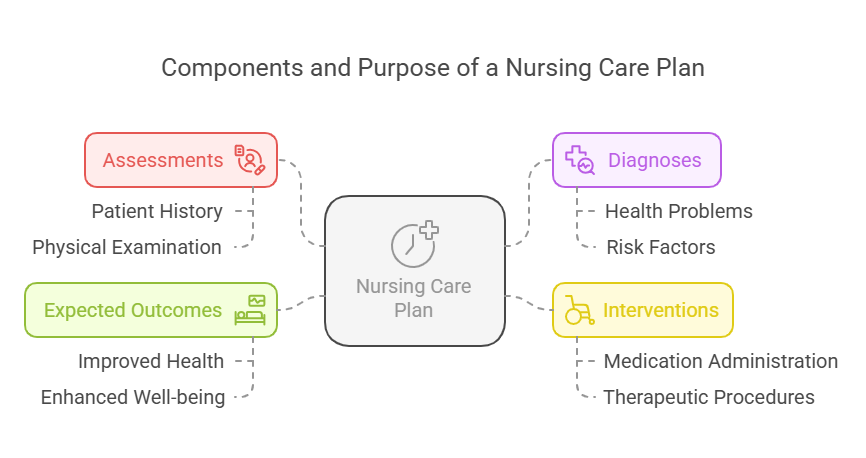
- Key Definitions:
- Care Plan: A detailed plan that outlines patient goals
and nursing interventions.
- Key Principles:
- Base care plans on comprehensive assessment data.
- Prioritize interventions to address the most critical needs.
- Take-Home Message: Care plans are tailored to meet
individual patient needs. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on the steps
involved in care planning. - Practice Question: What is the first step in developing a
care plan?- A) Setting goals
- B) Identifying nursing diagnoses
- C) Evaluating outcomes
- D) Implementing interventions
Correct Answer: B) Identifying nursing
diagnoses.
Rationale: This step is essential for guiding
the subsequent planning process.
1.3.4 Evaluate Outcomes
- Introduction: Evaluating outcomes is
crucial for determining the effectiveness of nursing interventions, ensuring
continuous improvement in patient care. - Key Definitions:
- Outcome Evaluation: The process of assessing whether care
goals were met.
- Key Principles:
- Regularly review patient progress against care plan goals.
- Adjust care plans based on evaluation findings.
- Take-Home Message: Outcome evaluation is key to effective
nursing practice. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions may focus on the
importance of outcome evaluation. - Practice Question: What should a nurse do if the expected
outcomes are not met?- A) Ignore the results
- B) Revise the care plan
- C) Document the failure
- D) Discharge the patient
Correct Answer: B) Revise the care plan.
Rationale: Adjustments are necessary to meet patient
needs effectively.
1.3.5 Interpret Findings
- Introduction: Interpreting
assessment findings is key to making informed clinical
decisions, requiring critical thinking and clinical judgment. - Key Definitions:
- Interpretation of Findings: Analyzing assessment data to
inform clinical decisions.
- Key Principles:
- Consider various factors, including patient history and cultural
background. - Use clinical judgment to guide decisions.
- Take-Home Message: Accurate interpretation of findings is
essential for effective diagnosis and care planning. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on factors
influencing the interpretation of assessment data. - Practice Question: Which of the following is an important
factor in interpreting assessment findings?- A) Personal biases
- B) Patient’s cultural background
- C) Previous experiences with similar cases
- D) All of the above
Correct Answer: D) All of the above.
Rationale: Each factor can influence how findings are
interpreted.
1.4 Documentation Standards
1.4.1 Accurate Record-Keeping
- Introduction: Accurate documentation is a
legal and ethical obligation for nurses, ensuring continuity of care and
protecting patient rights.
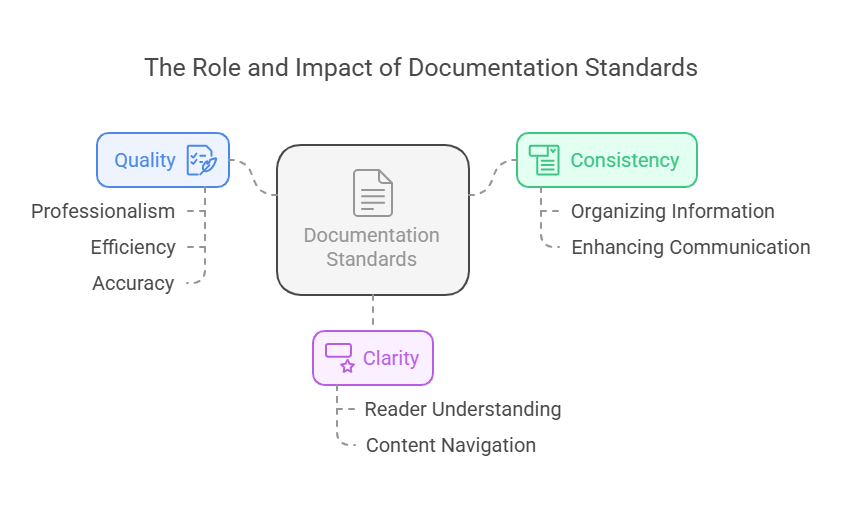
- Key Definitions:
- Record-Keeping: The process of documenting patient
assessments, interventions, and outcomes.
- Key Principles:
- Maintain detailed and accurate records to facilitate communication.
- Ensure documentation meets legal standards.
- Take-Home Message: Accurate record-keeping is essential for
effective patient care and legal protection. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions often focus on the
importance and standards of documentation. - Practice Question: What is the primary purpose of accurate
record-keeping in nursing?- A) To fulfill legal requirements
- B) To communicate with other healthcare providers
- C) To track patient progress
- D) All of the above
Correct Answer: D) All of the above.
Rationale: Each option reflects a critical aspect of
documentation.
1.4.2 Ethical Considerations in Data Collection
- Introduction: Ethical considerations are paramount in
health assessments, requiring nurses to respect patient confidentiality and
obtain informed consent. - Key Definitions:
- Ethical Data Collection: Gathering patient information
while upholding ethical standards.
- Key Principles:
- Ensure patient privacy during assessments.
- Obtain informed consent before collecting data.
- Take-Home Message: Ethical practices in data collection
uphold patient rights and trust. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on ethical
standards in nursing practice. - Practice Question: Which of the following is an ethical
consideration in data collection?- A) Collecting data without consent
- B) Sharing patient information with unauthorized individuals
- C) Ensuring patient privacy during assessments
- D) Ignoring patient preferences
Correct Answer: C) Ensuring patient privacy
during assessments.
Rationale: Respecting privacy is a
fundamental ethical obligation in nursing.”
2. Holistic Nursing Assessment
2.1 General Status and Vital Signs
2.1.1 General Appearance
2.1.1.1 Behavior
- Introduction: Observing a patient’s
behavior provides insights into their mental and emotional
state. This assessment is crucial for holistic care. - Key Definitions:
- Behavior: The way in which one acts or conducts oneself,
especially towards others.
- Key Principles:
- Behavioral observations can signal underlying mental health conditions.
- Understanding behavior guides further assessment and intervention.
- Take-Home Message: Behavioral assessments are vital for
identifying mental health issues. - PNLE Question: Which behavior may indicate a mental health
issue?- A) Calm demeanor
- B) Excessive fidgeting
- C) Engaging in conversation
- D) Following instructions
Correct Answer: B) Excessive fidgeting – This
may indicate anxiety or restlessness.
2.1.1.2 Grooming and Hygiene
- Introduction: Assessing grooming and
hygiene can reveal important information about a patient’s
self-care abilities and overall health. - Key Definitions:
- Grooming: The practice of maintaining personal hygiene
and appearance.
- Key Principles:
- Changes in grooming can reflect physical or psychological issues.
- Poor hygiene may indicate a decline in self-care abilities.
- Take-Home Message: Grooming and hygiene assessments are
essential for understanding a patient’s health status. - PNLE Question: Poor grooming may indicate which of the
following?- A) High socioeconomic status
- B) Mental health issues
- C) Good physical health
- D) Cultural practices
Correct Answer: B) Mental health issues – Poor
grooming can be a sign of depression or other mental health conditions.
2.1.1.3 Skin Integrity
- Introduction: Skin integrity is a vital
indicator of overall health. Assessing the skin can help identify potential
complications or health issues. - Key Definitions:
- Skin Integrity: The condition of the skin, including its
ability to remain intact and healthy.
- Key Principles:
- Regular skin assessments can help detect issues early.
- Compromised skin integrity can lead to infections or other complications.
- Take-Home Message: Skin assessments are crucial for
preventing complications and promoting health. - PNLE Question: Which finding would indicate compromised
skin integrity?- A) Smooth and intact skin
- B) Presence of pressure ulcers
- C) Healthy skin color
- D) Warm temperature
Correct Answer: B) Presence of pressure ulcers
– This indicates a breakdown in skin integrity.
2.1.2 Vital Signs
2.1.2.1 Blood Pressure
- Introduction: Blood pressure is a critical
vital sign that reflects cardiovascular health. Understanding its
significance is essential for patient assessment. - Key Definitions:
- Blood Pressure: The force of blood against the walls of
the arteries.
- Key Principles:
- Monitoring blood pressure helps identify hypertension or hypotension.
- Abnormal readings necessitate further assessment and management.
- Take-Home Message: Blood pressure monitoring is essential
for cardiovascular health assessment. - PNLE Question: What is considered a normal blood pressure
reading for adults?- A) 120/80 mmHg
- B) 140/90 mmHg
- C) 160/100 mmHg
- D) 100/60 mmHg
Correct Answer: A) 120/80 mmHg – This is the
standard normal range for adults.
2.1.2.2 Heart Rate
- Introduction: Heart rate is a key
indicator of cardiac function and overall health. Abnormal rates can signal
underlying conditions. - Key Definitions:
- Heart Rate: The number of heartbeats per minute.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding normal heart rate ranges aids in identifying potential
cardiac issues. - Abnormal heart rates require further evaluation.
- Take-Home Message: Monitoring heart rate is critical for
assessing cardiac health. - PNLE Question: What is the normal resting heart rate for
adults?- A) 60-100 beats per minute
- B) 40-60 beats per minute
- C) 100-120 beats per minute
- D) 80-120 beats per minute
Correct Answer: A) 60-100 beats per minute –
This range is considered normal for adults.
2.1.2.3 Respiratory Rate
- Introduction: The
respiratory rate provides insights into a patient’s
respiratory function and overall health status. It is a vital sign that
should be monitored regularly. - Key Definitions:
- Respiratory Rate: The number of breaths taken per minute.
- Key Principles:
- Monitoring respiratory rates helps detect respiratory distress or
abnormalities. - Abnormal rates may indicate underlying health issues.
- Take-Home Message: Regular monitoring of respiratory rates
is crucial for respiratory health assessment. - PNLE Question: What is the normal respiratory rate for
adults?- A) 10-20 breaths per minute
- B) 20-30 breaths per minute
- C) 30-40 breaths per minute
- D) 5-10 breaths per minute
Correct Answer: A) 10-20 breaths per minute –
This range is considered normal for adults.
2.1.2.4 Temperature
- Introduction: Body temperature is a
fundamental vital sign that indicates the body’s metabolic state. Abnormal
temperatures can signal infection or other health issues. - Key Definitions:
- Body Temperature: The measure of the body’s ability to
generate and dissipate heat.
- Key Principles:
- Regular temperature assessments are crucial for detecting fever or
hypothermia. - Abnormal temperatures necessitate further evaluation.
- Take-Home Message: Monitoring body temperature is essential
for identifying health issues. - PNLE Question: What is the normal oral temperature range
for adults?- A) 96.8-100.4°F
- B) 98.6-102.6°F
- C) 97.0-99.0°F
- D) 95.0-98.0°F
Correct Answer: A) 96.8-100.4°F – This range
is considered normal for oral temperature.
2.1.2.5 Pulse Oximetry
- Introduction: Pulse oximetry is a
non-invasive method to assess oxygen saturation levels in the blood. It is
essential for monitoring respiratory function. - Key Definitions:
- Pulse Oximetry: A test that measures the oxygen level
(oxygen saturation) of the blood.
- Key Principles:
- Monitoring oxygen saturation helps identify respiratory issues early.
- Low oxygen levels may require immediate intervention.
- Take-Home Message: Pulse oximetry is crucial for assessing
respiratory function. - PNLE Question: What is considered a normal oxygen
saturation level?- A) 85-90%
- B) 90-95%
- C) 95-100%
- D) 100-105%
Correct Answer: C) 95-100% – This range is considered normal
for oxygen saturation.
2.1.2.6 Interpretation of Findings
- Introduction: Interpreting vital sign findings is critical
for assessing patient health. Understanding normal ranges and deviations is
essential for effective care. - Key Definitions:
- Interpretation: The action of explaining the meaning of
something.
- Key Principles:
- Accurate interpretation of vital signs is essential for identifying health
issues. - Understanding deviations from normal ranges guides appropriate
interventions.
- Take-Home Message: Accurate interpretation of vital signs
is key to effective nursing care. - PNLE Question: A patient has a blood pressure of 150/95
mmHg. What does this indicate?- A) Normal blood pressure
- B) Hypotension
- C) Hypertension
- D) Bradycardia
Correct Answer: C) Hypertension – This reading
indicates high blood pressure.
2.2 Mental Status Assessment
2.2.1 Adults
2.2.1.1 Anxiety Disorders
- Introduction: Assessing for
anxiety disorders is crucial in understanding a patient’s
mental health. Recognizing symptoms can guide appropriate interventions.
- Key Definitions:
- Anxiety Disorders: A group of mental disorders
characterized by significant feelings of anxiety and fear.
- Key Principles:
- Identifying anxiety disorder symptoms allows for timely interventions.
- Understanding the impact of anxiety on daily functioning is essential.
- Take-Home Message: Early identification of anxiety
disorders is vital for effective mental health care. - PNLE Question: Which symptom is commonly associated with
anxiety disorders?- A) Euphoria
- B) Excessive worry
- C) Increased energy
- D) Social withdrawal
Correct Answer: B) Excessive worry – This is a
hallmark symptom of anxiety disorders.
2.2.1.2 Cognitive Disorders
- Introduction: Cognitive disorders impact a patient’s
ability to think, remember, and reason. Early identification is key to
managing these conditions.
- Key Definitions:
- Cognitive Disorders: Disorders that primarily affect
learning, memory, perception, and problem-solving.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding cognitive disorders helps nurses provide appropriate care.
- Early identification can improve patient outcomes.
- Take-Home Message: Recognizing cognitive disorders is
essential for effective nursing interventions. - PNLE Question: Which of the following is a common cognitive
disorder?- A) Depression
- B) Dementia
- C) Bipolar disorder
- D) Schizophrenia
Correct Answer: B) Dementia – This is a common
cognitive disorder affecting memory and thinking.
2.2.1.3 Mood Disorders
- Introduction: Mood disorders significantly
affect a patient’s emotional state. Recognizing these disorders is essential
for effective management.
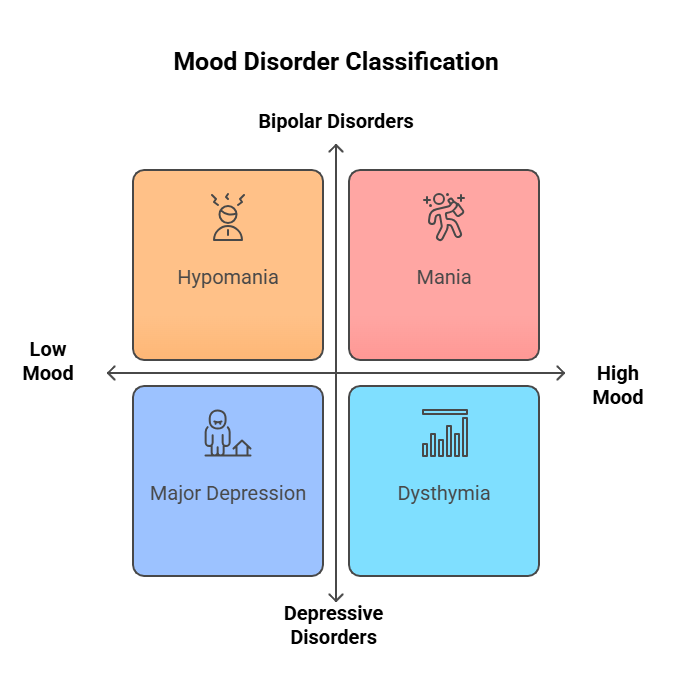
- Key Definitions:
- Mood Disorders: Psychological disorders characterized by
the elevation or lowering of a person’s mood.
- Key Principles:
- Identifying mood disorders enables nurses to implement appropriate
interventions. - Understanding the impact of mood on behavior is crucial.
- Take-Home Message: Early recognition of mood disorders is
vital for patient support. - PNLE Question: Which disorder is characterized by
alternating periods of depression and mania?- A) Major depressive disorder
- B) Generalized anxiety disorder
- C) Bipolar disorder
- D) Schizophrenia
Correct Answer: C) Bipolar disorder – This
disorder is marked by mood swings.
2.2.1.4 Suicide Risk
- Introduction: Assessing suicide risk is a
critical component of mental health evaluation. Early intervention can save
lives.
- Key Definitions:
- Suicide Risk: The likelihood that an individual will take
their own life.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding how to assess suicide risk is vital for providing timely
care. - Asking direct questions about suicidal thoughts can be lifesaving.
- Take-Home Message: Timely assessment of suicide risk is
essential for effective mental health care. - PNLE Question: Which question is most appropriate when
assessing suicide risk?- A) “”Do you feel sad?””
- B) “”Have you ever thought about hurting yourself?””
- C) “”What do you do for fun?””
- D) “”Are you feeling anxious?””
Correct Answer: B) “”Have you ever thought about hurting
yourself?”” – This directly addresses suicide risk.
2.2.2 Children and Adolescents
2.2.2.1 Developmental Screening Tools
- Introduction:
Developmental screening tools help assess children’s growth
and development. Early detection of issues can lead to timely interventions.
- Key Definitions:
- Developmental Screening Tools: Instruments used to assess
a child’s development in various domains.
- Key Principles:
- Utilizing these tools allows nurses to monitor children’s growth
effectively. - Early identification of developmental delays is crucial for intervention.
- Take-Home Message: Developmental screening is essential for
promoting healthy child development. - PNLE Question: What is the primary purpose of developmental
screening tools?- A) To diagnose mental disorders
- B) To assess physical health
- C) To identify developmental delays
- D) To evaluate academic performance
Correct Answer: C) To identify developmental delays – This is
the primary purpose of these tools.
2.2.2.2 Behavioral Issues
- Introduction: Assessing
behavioral issues in children and adolescents is essential
for understanding their mental health needs. Early identification can guide
interventions. - Key Definitions:
- Behavioral Issues: Problems related to a child’s behavior
that may affect their social, emotional, or academic functioning.
- Key Principles:
- Identifying behavioral issues allows for timely support and interventions.
- Understanding the context of behaviors is crucial for effective
assessment.
- Take-Home Message: Early identification of behavioral
issues is vital for promoting healthy development. - PNLE Question: Which behavior may indicate a behavioral
issue in children?- A) Cooperation with peers
- B) Frequent tantrums
- C) Interest in activities
- D) Good academic performance
Correct Answer: B) Frequent tantrums – This may indicate
underlying behavioral issues.
2.3 Psychosocial, Cognitive, and Moral Development
2.3.1 Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
- Introduction: Piaget’s theory outlines the
stages of cognitive development in children. Understanding these stages aids
in assessing children’s learning and behavior. - Key Definitions:
- Cognitive Development: The process of growth and change
in intellectual/mental abilities.
- Key Principles:
- Knowledge of Piaget’s stages helps tailor interventions to children’s
cognitive abilities. - Each stage represents a different way of thinking and understanding the
world.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding Piaget’s stages is
essential for effective child assessment. - PNLE Question: At what stage do children begin to think
logically about concrete events?- A) Sensorimotor
- B) Preoperational
- C) Concrete operational
- D) Formal operational
Correct Answer: C) Concrete operational – This
stage is characterized by logical thinking about concrete objects.
2.3.2 Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development
- Introduction: Kohlberg’s theory describes
the progression of moral reasoning. Understanding these stages can inform
ethical decision-making in nursing. - Key Definitions:
- Moral Development: The process through which individuals
develop proper attitudes and behaviors toward other people in society.
- Key Principles:
- Recognizing the stages of moral development aids in understanding
patients’ ethical perspectives. - Each stage reflects a different level of moral reasoning.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding Kohlberg’s stages enhances
ethical decision-making in nursing. - PNLE Question: At what stage do individuals base their
moral decisions on social contracts and individual rights?- A) Pre-conventional
- B) Conventional
- C) Post-conventional
- D) Universal ethical principles
Correct Answer: C) Post-conventional – This
stage involves reasoning based on social contracts and individual rights.
2.3.3 Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
- Introduction: Erikson’s theory outlines
the psychosocial challenges faced at different life stages. Understanding
these can enhance patient care and support. - Key Definitions:
- Psychosocial Development: The development of personality
and social relationships.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding Erikson’s stages helps provide appropriate support for
patients navigating psychosocial challenges. - Each stage presents a conflict that must be resolved for healthy
development.
- Take-Home Message: Recognizing Erikson’s stages is crucial
for understanding patient needs. - PNLE Question: What is the primary psychosocial challenge
during adolescence according to Erikson?- A) Trust vs. mistrust
- B) Identity vs. role confusion
- C) Intimacy vs. isolation
- D) Integrity vs. despair
Correct Answer: B) Identity vs. role confusion – This stage
focuses on developing a personal identity.”
3. Pain Assessment and Management
3.1 Types of Pain
3.1.1 Acute Pain
- Introduction: Acute pain is a
sudden onset of discomfort that typically signals
injury or illness. Understanding its
characteristics is vital for effective management. - Key Definitions:
- Acute Pain: Pain that lasts for a short duration, often
associated with a specific injury or illness.
- Key Principles:
- Rapid onset and usually resolves with treatment.
- Serves as a protective mechanism.
- PNLE Question: Which of the following is a common cause of
acute pain?- A) Chronic illness
- B) Surgery
- C) Psychological factors
- D) Aging
Correct Answer: B) Surgery
Rationale: Surgical procedures often lead to acute pain as a
direct result of tissue injury.
- Topic Overview: Recognizing the nature of acute pain allows
nurses to implement timely interventions for relief.
3.1.2 Chronic Pain
- Introduction: Chronic pain persists over time and can
significantly impact quality of life. Understanding its
management is crucial for nursing practice. - Key Definitions:
- Chronic Pain: Pain that lasts longer than three months
and may not have a clear cause.
- Key Principles:
- Often requires a multidisciplinary approach for management.
- Can lead to psychological issues such as depression.
- PNLE Question: Which characteristic distinguishes chronic
pain from acute pain?- A) Duration of less than three months
- B) Associated with a specific injury
- C) Lasts longer than three months
- D) Resolves with treatment
Correct Answer: C) Lasts longer than three
months Rationale: Chronic pain is defined by its prolonged
duration, unlike acute pain.
- Topic Overview: Identifying chronic pain requires a
comprehensive approach to management, focusing on improving the patient’s
quality of life.
3.1.3 Neuropathic Pain
- Introduction: Neuropathic pain results from
nerve damage and can be challenging to manage.
Understanding its characteristics is essential for effective care. - Key Definitions:
- Neuropathic Pain: Pain caused by damage or disease
affecting the nervous system.
- Key Principles:
- Often described as burning, shooting, or tingling.
- May require specific pharmacological interventions.
- PNLE Question: Which condition is commonly associated with
neuropathic pain?- A) Osteoarthritis
- B) Diabetes
- C) Migraine
- D) Fibromyalgia
- Correct Answer: B) Diabetes
- Rationale: Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication
of diabetes that leads to neuropathic pain.
- Topic Overview: Recognizing neuropathic pain is crucial for
implementing appropriate pharmacological and non-pharmacological
interventions.
3.2 Pain Assessment Techniques
3.2.1 Pain Intensity, Location, Duration
- Introduction: Accurately assessing pain
intensity, location, and
duration is essential for effective management. This
information guides treatment decisions.
- Key Definitions:
- Pain Intensity: A measure of how severe the pain is.
- Pain Location: The specific area of the body where pain
is felt. - Pain Duration: The length of time the pain has been
experienced.
- Key Principles:
- Use of standardized scales enhances assessment accuracy.
- PNLE Question: Which scale is commonly used to assess pain
intensity?- A) Numeric Rating Scale (NRS)
- B) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
- C) Apgar Score
- D) Barthel Index
- Correct Answer: A) Numeric Rating Scale (NRS)
- Rationale: The NRS is a widely used tool for patients to
rate their pain on a scale of 0 to 10.
- Topic Overview: Utilizing pain assessment tools enables
nurses to quantify pain and tailor interventions accordingly.
3.2.2 Pain Documentation
- Introduction: Proper documentation of pain assessments is
critical for continuity of care. It ensures that all
healthcare providers are informed of the patient’s status.
- Key Definitions:
- Pain Documentation: The process of recording pain
assessments and management strategies.
- Key Principles:
- Consistent documentation improves communication among healthcare team
members.
- PNLE Question: What should be included in pain
documentation?- A) Patient’s pain history
- B) Assessment findings
- C) Interventions and patient responses
- D) All of the above
- Correct Answer: D) All of the above
- Rationale: Comprehensive documentation includes all
relevant information to ensure effective care.
- Topic Overview: Comprehensive documentation of pain
assessments and management strategies is vital for effective patient care.
3.3 Pain Management Strategies
3.3.1 Pharmacological Interventions
- Introduction: Pharmacological interventions are a
cornerstone of pain management. Understanding the various options is
essential for effective treatment.
- Key Definitions:
- Pharmacological Interventions: Medications used to
relieve pain.
- Key Principles:
- Different classes of medications target different types of pain.
- PNLE Question: Which class of medication is commonly used
for managing acute pain?- A) Antidepressants
- B) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- C) Anticonvulsants
- D) Muscle relaxants
Correct Answer: B) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs) Rationale: NSAIDs are commonly used to reduce
inflammation and relieve acute pain.
- Topic Overview: Knowledge of pharmacological options allows
nurses to provide effective pain relief while monitoring for side effects.
3.3.2 Non-pharmacological Strategies
- Introduction: Non-pharmacological strategies can complement
pharmacological interventions in pain management. These approaches are
essential for holistic care.
- Key Definitions:
- Non-pharmacological Strategies: Techniques that do not
involve medication, such as physical therapy and relaxation techniques.
- Key Principles:
- Can enhance the effectiveness of pharmacological treatments.
- PNLE Question: Which of the following is a
non-pharmacological pain management strategy?- A) Opioids
- B) Massage therapy
- C) Corticosteroids
- D) Antidepressants
Correct Answer: B) Massage therapy
Rationale: Massage therapy is a recognized non-pharmacological
approach to relieve pain and promote relaxation.
- Topic Overview: Implementing non-pharmacological strategies
can enhance pain relief and improve patient satisfaction.
3.3.3 Adjuvants
- Introduction: Adjuvant medications play a crucial role in
managing pain, particularly in chronic conditions. Understanding their use
is essential for effective care. - Key Definitions:
- Adjuvant Medications: Drugs that are not primarily
designed to control pain but can enhance pain relief when used in
conjunction with other medications.
- Key Principles:
- Often used in combination with analgesics for better pain control.
- PNLE Question: Which of the following is considered an
adjuvant medication for pain management?- A) Acetaminophen
- B) Gabapentin
- C) Ibuprofen
- D) Morphine
Correct Answer: B) Gabapentin
Rationale: Gabapentin is commonly used as an adjuvant for
neuropathic pain management.
- Topic Overview: Recognizing the role of adjuvants in pain
management allows nurses to optimize treatment plans for patients.
Take-Home Message
Understanding the types of pain, assessment techniques, and management
strategies is essential for effective nursing care and improving patient
outcomes.” “
4. Indicators of Violence and Abuse
4.1 Types of Abuse
4.1.1 Physical Abuse
- Introduction: Physical abuse involves the use of
force that results in injury or
harm. Recognizing the signs is crucial for protecting
vulnerable individuals and ensuring their safety. - Key Definitions:
- Physical Abuse: Intentional infliction of bodily harm or
injury. - Indicators: Signs that may suggest abuse, such as
unexplained injuries.
- Key Principles:
- Awareness of common signs (e.g., bruises, fractures).
- Importance of documentation and timely intervention.
- Take-Home Message: Recognizing physical abuse is essential
for safeguarding individuals and initiating appropriate actions. - PNLE Question: Which of the following is a common indicator
of physical abuse?- A) Unexplained bruises or injuries
- B) Changes in appetite
- C) Withdrawal from social activities
- D) Poor hygiene
Correct Answer: A) Unexplained bruises or
injuries.
Rationale: Unexplained injuries are a primary
indicator of physical abuse.
4.1.2 Emotional Abuse
- Introduction: Emotional abuse can have profound effects on
mental health. Understanding its indicators is essential
for providing support and intervention. - Key Definitions:
- Emotional Abuse: Psychological harm caused by verbal or
non-verbal behaviors. - Indicators: Signs that may suggest emotional distress,
such as withdrawal or anxiety.
- Key Principles:
- Recognizing behavioral changes (e.g., isolation).
- Importance of supportive interventions.
- Take-Home Message: Identifying emotional abuse is vital for
addressing the psychological needs of affected individuals. - PNLE Question: Which behavior may suggest emotional abuse?
- A) Frequent compliments
- B) Isolation from friends and family
- C) Open communication
- D) Participation in activities
Correct Answer: B) Isolation from friends and
family.
Rationale: Isolation is a common sign of
emotional abuse.
4.1.3 Sexual Abuse
- Introduction: Sexual abuse is a violation of an
individual’s rights and can lead to lasting
trauma. Awareness of its signs is crucial for timely
intervention. - Key Definitions:
- Sexual Abuse: Non-consensual sexual acts or exploitation.
- Indicators: Behavioral changes, physical signs, or
emotional distress.
- Key Principles:
- Recognizing sudden changes in behavior.
- Importance of confidentiality and support.
- Take-Home Message: Identifying potential signs of sexual
abuse allows for timely support and intervention for affected individuals. - PNLE Question: Which of the following may indicate sexual
abuse?- A) Sudden changes in behavior
- B) Good academic performance
- C) Healthy relationships
- D) Active participation in sports
Correct Answer: A) Sudden changes in behavior.
Rationale</strong >: Behavioral changes can indicate trauma from sexual abuse.
4.1.4 Neglect
- Introduction: Neglect occurs when an individual’s
basic needs are not met. Recognizing the signs is essential
for protecting vulnerable populations. - Key Definitions:
- Neglect: Failure to provide necessary care, leading to
harm. - Indicators: Poor hygiene, malnutrition, or lack of
supervision.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding the impact of neglect on health.
- Importance of advocacy for resources.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding the signs of neglect
enables nurses to advocate for individuals in need of support and resources. - PNLE Question: Which of the following is a common indicator
of neglect?- A) Well-groomed appearance
- B) Frequent absences from school
- C) Active participation in community events
- D) Healthy weight
Correct Answer: B) Frequent absences from
school.
Rationale: Frequent absences can indicate neglect
in a child’s care.
4.2 Reporting and Intervention
4.2.1 Child Abuse
- Introduction: Reporting child abuse is a
legal and ethical obligation for nurses.
Understanding the signs and reporting protocols is essential for protecting
children. - Key Definitions:
- Child Abuse: Any act that results in harm or potential
harm to a child. - Reporting Protocols: Steps to take when abuse is
suspected.
- Key Principles:
- Importance of documentation and timely reporting.
- Understanding confidentiality and legal obligations.
- Take-Home Message: Nurses play a crucial role in
identifying and reporting child abuse, ensuring the safety and well-being of
vulnerable children. - PNLE Question: What is the nurse’s responsibility when
suspecting child abuse?- A) Confront the parents
- B) Document findings and report to authorities
- C) Ignore the signs
- D) Discuss with the child
Correct Answer: B) Document findings and
report to authorities.
Rationale: Documenting and
reporting is essential for legal compliance and child protection.
4.2.2 Domestic Violence
- Introduction: Domestic violence is a serious issue that
affects individuals across all demographics. Recognizing its signs is vital
for intervention and support. - Key Definitions:
- Domestic Violence: Abuse occurring within intimate
relationships. - Indicators: Physical injuries, emotional distress, or
isolation.
- Key Principles:
- Importance of safety planning for victims.
- Understanding resources available for support.
- Take-Home Message: Identifying signs of domestic violence
allows nurses to provide appropriate support and resources to affected
individuals. - PNLE Question: Which of the following is a common sign of
domestic violence?- A) Open communication
- B) Frequent injuries with vague explanations
- C) Supportive relationships
- D) Active social life
Correct Answer: B) Frequent injuries with
vague explanations.
Rationale: Vague explanations for
injuries often indicate domestic violence.
4.2.3 Mandatory Reporting
- Introduction: Mandatory reporting laws require nurses to
report suspected abuse or neglect.
Understanding these laws is essential for legal compliance and ethical
practice. - Key Definitions:
- Mandatory Reporting: Legal requirement to report
suspected abuse. - Indicators: Signs that necessitate reporting, such as
unexplained injuries.
- Key Principles:
- Understanding the legal ramifications of failing to
report. - Importance of training on reporting procedures.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding mandatory reporting
requirements ensures that nurses fulfill their legal and ethical obligations
to protect vulnerable individuals. - PNLE Question: Which of the following situations requires
mandatory reporting?- A) A patient discloses past trauma
- B) A child presents with unexplained injuries
- C) A patient expresses sadness
- D) A patient has a chronic illness
Correct Answer: B) A child presents with
unexplained injuries.
Rationale: Unexplained injuries in
a child necessitate mandatory reporting.
Quick Tips:
- Always document signs of abuse meticulously.
- Familiarize yourself with local reporting laws and protocols.
- Maintain a supportive and non-judgmental approach when discussing potential
abuse with patients.
Common Misconceptions:
- Misconception: Only physical signs indicate abuse.
- Clarification: Emotional and psychological signs are
equally important and should not be overlooked.
Memory Aid:
- Mnemonic for Types of Abuse:
PENS (Physical, Emotional, Neglect, Sexual) – Remember the
different types of abuse to ensure comprehensive assessment and
intervention.”
5. Cultural and Spiritual Considerations
5.1 Cultural Beliefs and Practices
5.1.1 Health Beliefs
- Introduction: Cultural beliefs significantly influence
health practices and perceptions. Understanding these beliefs is essential
for providing culturally competent care. - Key Definitions:
- Cultural Beliefs: Shared ideas and values that influence
health behaviors and perceptions within a specific cultural group. - Culturally Competent Care: Care that respects and
integrates a patient’s cultural beliefs and practices.
- Key Principles:
- Recognizing diverse health beliefs allows for tailored care approaches.
- Respecting cultural differences enhances patient trust and engagement.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding cultural health beliefs is
crucial for delivering effective and respectful nursing care. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions often focus on
identifying cultural health beliefs and their implications for nursing
practice. - Practice Question: Which of the following is an example of
a cultural health belief?- A) Belief in modern medicine
- B) Preference for herbal remedies
- C) Acceptance of vaccinations
- D) Reliance on surgery
Correct Answer: B) Preference for herbal remedies.
Rationale: This option reflects a cultural perspective on
health that may differ from conventional medical practices.
5.1.2 Dietary Customs
- Introduction: Dietary customs vary widely across cultures
and can impact nutritional health. Understanding these customs is crucial
for effective dietary assessments. - Key Definitions:
- Dietary Customs: Traditional eating habits and food
preferences shaped by cultural beliefs and practices.
- Key Principles:
- Awareness of dietary restrictions and preferences is essential for
nutritional assessments. - Culturally sensitive dietary guidance promotes better health outcomes.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding dietary customs enables
nurses to provide appropriate nutritional guidance and support. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions about how
dietary customs influence patient nutrition and care. - Practice Question: Which of the following dietary customs
may affect a patient’s nutrition?- A) Preference for fast food
- B) Vegetarianism
- C) High sugar intake
- D) All of the above
Correct Answer: D) All of the above.
Rationale</strong >: Each option represents a dietary custom that can significantly affect
nutrition.
5.2 Cultural Competence
5.2.1 Awareness and Sensitivity
- Introduction: Cultural competence involves understanding
and respecting diverse cultural backgrounds. This awareness is essential for
effective patient care. - Key Definitions:
- Cultural Competence: The ability to interact effectively
with people of different cultures.
- Key Principles:
- Self-reflection on personal biases is crucial for developing cultural
competence. - Continuous education about different cultures enhances care quality.
- Take-Home Message: Developing cultural competence requires
ongoing self-reflection and education to provide respectful and effective
care. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions may assess
understanding of cultural competence and its application in nursing. - Practice Question: What is the first step in developing
cultural competence?- A) Learning about other cultures
- B) Self-reflection on personal biases
- C) Attending cultural events
- D) Engaging with diverse populations
Correct Answer: B) Self-reflection on personal biases.
Rationale: Self-awareness is foundational to
understanding and respecting cultural differences.
5.2.2 Adaptation of Care
- Introduction: Adapting care to meet cultural needs is
essential for patient satisfaction and outcomes. Nurses must be flexible in
their approaches. - Key Definitions:
- Adaptation of Care: Modifying nursing interventions to
align with a patient’s cultural values and preferences.
- Key Principles:
- Culturally relevant care improves patient engagement.
- Flexibility in care approaches fosters better health outcomes.
- Take-Home Message: Tailoring care to align with cultural
values enhances patient engagement and satisfaction. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on how to
adapt nursing care to meet cultural needs. - Practice Question: Which of the following is an example of
adapting care to cultural needs?- A) Ignoring patient preferences
- B) Providing care in a culturally relevant manner
- C) Standardizing all care approaches
- D) Focusing solely on medical interventions
Correct Answer: B) Providing care in a culturally relevant
manner.
Rationale: This option reflects a commitment to
respecting and integrating cultural preferences in care.
5.3 Spiritual Assessment
5.3.1 Beliefs and Practices
- Introduction: Spiritual beliefs can significantly impact
health and well-being. Assessing these beliefs is essential for holistic
care. - Key Definitions:
- Spiritual Beliefs: Personal beliefs that provide meaning
and purpose in life, which can influence health behaviors.
- Key Principles:
- Assessing spiritual beliefs is vital for holistic patient care.
- Understanding these beliefs can guide nursing interventions.
- Take-Home Message: Understanding patients’ spiritual
beliefs allows nurses to provide compassionate and holistic care. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Questions may focus on the
importance of spiritual assessments in nursing practice. - Practice Question: Which question is appropriate for
assessing a patient’s spiritual beliefs?- A) “”Do you believe in God?””
- B) “”What gives your life meaning?””
- C) “”Are you religious?””
- D) “”Do you attend church regularly?””
Correct Answer: B) “”What gives your life meaning?””
Rationale: This question invites a broader understanding
of the patient’s spirituality beyond religious affiliation.
5.3.2 Spiritual Care Interventions
- Introduction: Spiritual care interventions can enhance
patient well-being. Nurses play a vital role in providing this support. - Key Definitions:
- Spiritual Care Interventions: Actions taken by nurses to
support a patient’s spiritual needs and well-being.
- Key Principles:
- Implementing spiritual care can improve emotional and psychological
well-being. - Nurses should be trained to recognize and address spiritual needs.
- Take-Home Message: Implementing spiritual care
interventions can improve patients’ emotional and psychological well-being. - Relevance to the PNLE Exam: Expect questions on the role of
spiritual care in nursing practice. - Practice Question: Which of the following is a spiritual
care intervention?- A) Offering prayer
- B) Providing medical treatment
- C) Conducting physical assessments
- D) Documenting patient history
Correct Answer: A) Offering prayer.
Rationale</strong >: Offering prayer is a direct spiritual care intervention that can support a
patient’s spiritual needs.
6. Nutritional Assessment
- Introduction: Nutritional assessment is a systematic
approach to evaluating an individual’s dietary intake and nutritional
status. It is crucial for identifying potential health risks and guiding
dietary interventions, particularly in nursing practice.
- Key Definitions:
- Anthropometric Measures: Techniques used to measure the
physical dimensions and composition of the body, including height, weight,
and body mass index (BMI). - Waist-to-Hip Ratio: A measurement that compares the
circumference of the waist to that of the hips, indicating body fat
distribution. - Macronutrients: Nutrients required in large amounts for
energy and growth, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. - Micronutrients: Essential vitamins and minerals needed in
smaller amounts for various bodily functions.
- Key Principles:
- Accurate anthropometric measures are vital for assessing
nutritional status and identifying potential health issues. - The waist-to-hip ratio serves as an important indicator
of body fat distribution and associated health risks. - Analyzing macronutrient and micronutrient intake is
essential for determining dietary adequacy and guiding nutritional
interventions. - The 24-hour diet recall is a useful tool for assessing
dietary habits, though it has limitations in representing long-term
intake.
- Take-Home Message: Effective nutritional assessment is
essential for identifying health risks and implementing appropriate dietary
interventions in nursing practice.
6.1 Anthropometric Measures
6.1.1 Height, Weight, BMI
- Introduction: Anthropometric measures are essential for
assessing nutritional status. They provide valuable data for health
evaluations. - Key Definitions:
- BMI (Body Mass Index): A measure calculated using height
and weight to classify individuals into categories such as underweight,
normal weight, overweight, and obese.
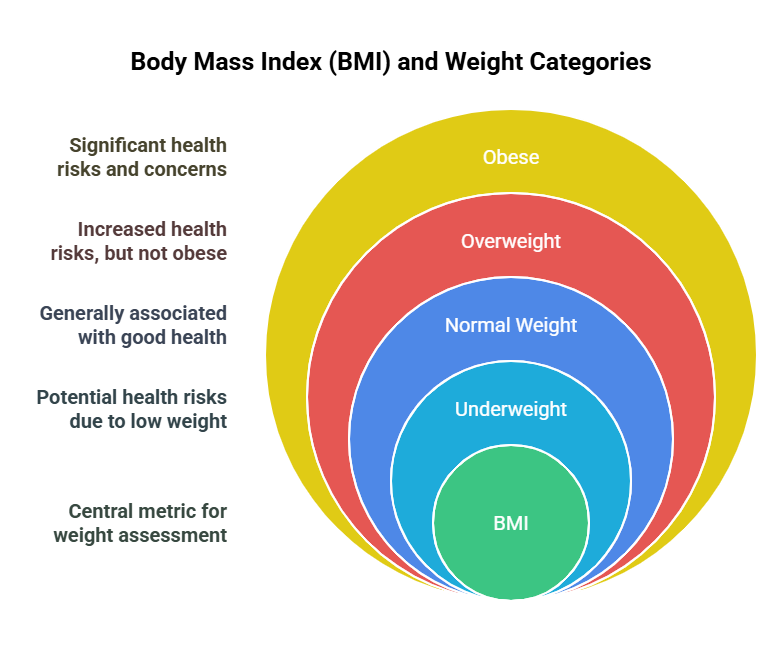
- PNLE Question: What is the formula for calculating Body
Mass Index (BMI)?- A) Weight (kg) / Height (m)
- B) Weight (kg) / Height (m²) (Correct Answer)
- C) Height (m) / Weight (kg)
- D) Height (m²) / Weight (kg)
- Topic Overview: Understanding anthropometric measures
allows nurses to assess and monitor patients’ nutritional health
effectively.
6.1.2 Waist-to-Hip Ratio
- Introduction: The waist-to-hip ratio is a useful measure of
body fat distribution. It can indicate risks for various health conditions. - Key Definitions:
- Waist-to-Hip Ratio: A calculation that helps assess the
distribution of body fat, which can be a predictor of cardiovascular
health risks.
- PNLE Question: What does a high waist-to-hip ratio
indicate?- A) Low risk of cardiovascular disease
- B) Increased risk of metabolic syndrome
(Correct Answer) - C) Healthy body composition
- D) Normal weight
- Topic Overview: Monitoring waist-to-hip ratios helps
identify patients at risk for obesity-related health issues.
6.2 Dietary Intake Analysis
6.2.1 Macronutrient and Micronutrient Intake
- Introduction: Analyzing macronutrient and micronutrient
intake is crucial for assessing dietary adequacy. This analysis informs
nutritional interventions.
- Key Definitions:
- Macronutrients: Nutrients that provide energy and are
required in larger quantities, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. - Micronutrients: Essential vitamins and minerals needed
for various bodily functions.
- PNLE Question: Which of the following is a macronutrient?
- A) Vitamin C
- B) Iron
- C) Protein (Correct Answer)
- D) Calcium
- Topic Overview: Understanding macronutrient and
micronutrient needs helps nurses provide effective dietary guidance and
support.
6.2.2 24-Hour Diet Recall
- Introduction: The 24-hour diet recall is a common method
for assessing dietary intake. It provides insights into patients’ eating
habits. - Key Definitions:
- 24-Hour Diet Recall: A method where patients report all
foods and beverages consumed in the past 24 hours to assess dietary
intake.
- PNLE Question: What is the primary limitation of a 24-hour
diet recall?- A) It is time-consuming
- B) It may not represent typical intake (Correct Answer)
- C) It requires specialized training
- D) It is difficult to analyze
- Topic Overview: While useful, the 24-hour diet recall may
not capture long-term dietary patterns, necessitating additional assessment
methods.
6.3 Nutritional Deficiencies
6.3.1 Protein-energy Malnutrition
- Introduction: Protein-energy malnutrition is a significant
concern, particularly in vulnerable populations. Recognizing its signs is
essential for timely intervention.
- Key Definitions:
- Protein-energy Malnutrition: A condition resulting from
inadequate intake of protein and calories, leading to various health
issues.
- PNLE Question: Which of the following is a common sign of
protein-energy malnutrition?- A) Healthy weight
- B) Edema (Correct Answer)
- C) Increased energy levels
- D) Strong immune function
- Topic Overview: Identifying signs of protein-energy
malnutrition enables nurses to implement appropriate nutritional
interventions.
6.3.2 Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies
- Introduction: Vitamin and mineral deficiencies can lead to
various health issues. Understanding their signs and symptoms is crucial for
effective care.
- Key Definitions:
- Vitamin Deficiency: A lack of essential vitamins in the
diet, leading to health problems. - Mineral Deficiency: A lack of essential minerals in the
diet, which can impact bodily functions.
- PNLE Question: Which deficiency is associated with scurvy?
- A) Vitamin A
- B) Vitamin C (Correct Answer)
- C) Vitamin D
- D) Vitamin B12
- Topic Overview: Recognizing vitamin and mineral
deficiencies allows nurses to provide targeted dietary recommendations and
interventions.
Quick Tips:
- Remember the BMI formula: Weight (kg) / Height (m²).
- A high waist-to-hip ratio signals increased health risks.
- Use the 24-hour diet recall for quick dietary assessments, but be aware of
its limitations.
Common Misconceptions:
- Many believe that BMI is a perfect measure of health; however, it does not
account for muscle mass or fat distribution. - Some think all fats are bad; however, healthy fats are essential for a
balanced diet.
Memory Aid:
- Use the mnemonic “”P-M-M”” for
Protein, Macronutrients, and Micronutrients to remember the
key components of dietary analysis.
Relevance to the PNLE Exam:
- Nutritional assessment concepts are frequently tested, especially questions
related to BMI calculations, dietary recalls, and recognizing signs of
deficiencies.”


























